- LSA Type-3 Filtering extends the ability of an ABR that is running the OSPF protocol to filter type-3 link state advertisement (LSAs) that are sent between different OSPF areas
- It allows only packets with specific prefixes to be sent from one area to another area and restricts all packets with other prefixes.
- It can be applied in or out of a specific OSPF area
GOAL
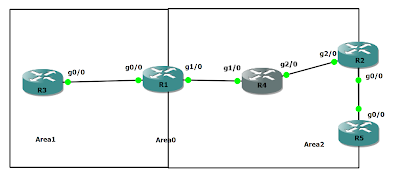
- R1's loopback address 150.1.1.1 must not access from area 1' devices except ABR.
- R1's other ip addresses must access from area's devices
- Step- 1 Create prefix-list
- Step- 2 Apply prefix-list to " under ospf routing process"
CONFIGURATION
Router2 (config) # ip prefix-list TEST seq 15 deny 150.1.1.1/32
Router2 (config) # ip prefix-list TEST seq 16 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
Router2 (config) # router ospf 1
Router2 (config-router) # area 1 filter-list prefix TEST in
Configuration at R2
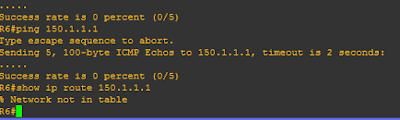
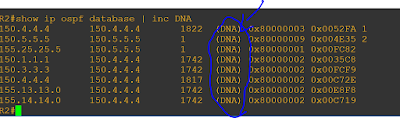
Verification R6 and R4 (Tried to ping 150.1.1.1)
Reference
Cisco OSPF Type3 LSA Filtering
INE_OSPF_Type3 Filtering